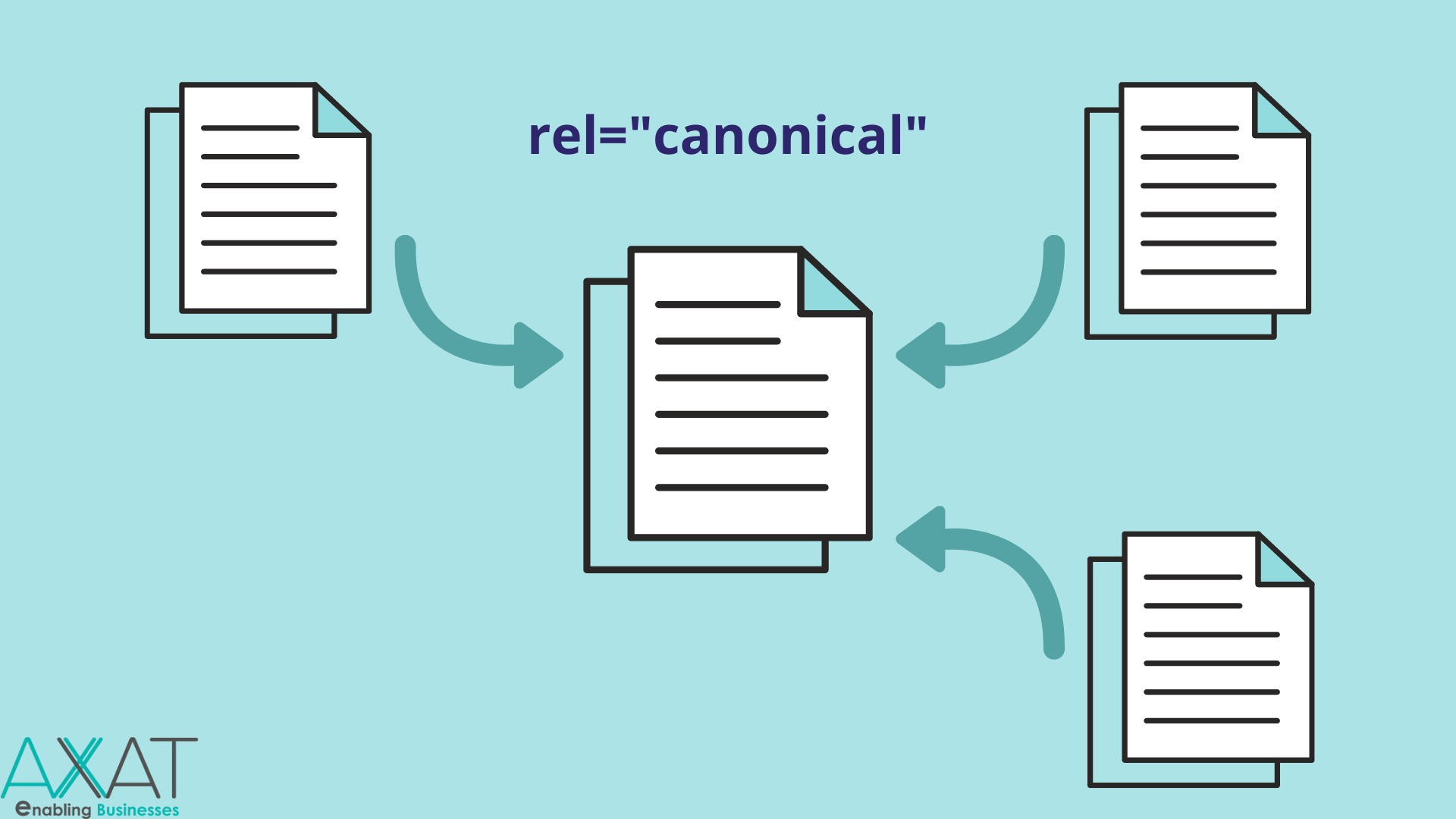
A canonical tag, also known as rel=canonical, is a small piece of HTML code that enables search engines to distinguish between the "primary" version of a website and all other sites that are either identical to it or very similar to it.
Canonical tags are used in SEO to inform Google which version of the page you want to show up in search results, to combine link equity from duplicate pages, and to enhance crawling and indexing of your website.
Here is an example of a canonical tag on a website:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.axattechnologies.com/blog/digital-marketing-for-any-type-of-website" />
What makes canonical tags important for SEO?
The canonical tag's major function is to inform search engines which page is the main, original version and which are simply duplicated with the same design.
Websites typically contain at least a few duplicate pages or pages that display the same content but have different URLs.
In these situations, Google must choose which website to index and rank because it won't utilize all of the pages as search results because they are all the same or very similar.
The canonical tag performs a core purpose, but it also has some important SEO benefits.
1. They complement PageRank
Canonical tags assist in combining all duplicate pages' link equity (PageRank) into the main, canonical page.
Backlinks from different external sources, such as users on social media or links from random websites, can frequently be obtained by duplicate pages.
As a result, these pages partially replace the primary version of the page, which is the one you truly want to rank as a search result, in terms of link equity.
Canonical tags allow for the transfer of PageRank from duplicate pages into a single URL, raising that URL's overall ranking in Google Search.
2. They assist in managing syndicated content.
Search engines can be informed by canonical tags which websites host the original content and which websites simply repost it (or syndicate).
Many website owners post their content on other websites (either for promotional or other purposes).
In this situation, Google must determine which website is the actual source of this content and should be presented as a search result, as opposed to which websites are only sharing it.
This issue is solved and the main, original version of the page is promoted in Google Search by using canonical tags on these external websites.
3. They help to crawl
Instead of duplicate pages that shouldn't be crawled at all, canonical tags enable search engines like Google to efficiently crawl and index the pages that you actually want to crawl and index.
By designating canonical pages, Google will concentrate more of its crawl money on the pages that are most important.
How can a canonical tag be added?
It's really simple to add rel="canonical" tags to your pages; just go to any duplicate webpage and do so in the head> section.
The main, original version should be the destination of the link in the canonical tag.
It is better to implement canonical tags one page at a time. On large websites, this can be impossible or take a lot of time and resources.
Thankfully, canonical tags can also be applied automatically by using a variety of plugins, including Yoast SEO (for WordPress).
What to avoid with canonical tags?
1. Multiple Canonicals on a single page
Pay attention to any multiple canonical tags that may unintentionally appear in the HTML of a page.
Even though it is uncommon, having more than one canonical tag on a page may cause the search engine to become confused and ignore this canonical signal.
2. On non-duplicates, avoid canonicals.
When using canonical tags, you should always make sure that the content on the duplicate pages and the main version of the page is either identical or at least very similar.
Search engines may become confused or overlook canonical tags if they are used on completely unrelated pages:
3. Don’t block canonicals via robots.txt
You should never block URLs with canonical tags by robots.txt file.
Robots.txt will stop Google from indexing the duplicate pages, making it impossible for it to see the canonical tag pointing to the primary version of the page.
Additionally, blocking URLs with canonical tags will stop PageRank from being transmitted to your primary versions.
4. Canonical should not be used in the <body>.
Canonical tags should never be used anywhere else in the HTML text than the <head> section of your sites.
Your canonical tags in the <body> section or elsewhere will be completely ignored by Google.
Final Thoughts
It’s not mandatory to use add a canonical tag on a page, but it is usually a good practice to add a tag to a page that points to itself. You can prevent unintentional errors or wrong canonical URL interpretations by a search engine by using absolute URLs in canonical tags.